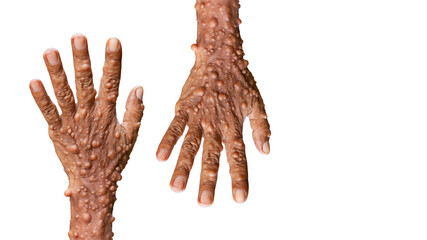
Neurofibromatosis (NF) is a genetic disorder that primarily affects the nervous system and can lead to the growth of tumors along nerve pathways.
There are two main types of neurofibromatosis: type 1 (NF1) and type 2 (NF2), each with its own set of symptoms and impacts on the body.
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1):
NF1 is the more common type of neurofibromatosis and is caused by mutations in the NF1 gene. It primarily affects the skin, nerves, bones, and may also affect other organs. Some ways NF1 can affect the body include:
- Skin Abnormalities: Café-au-lait spots (light brown spots on the skin), freckling in the armpits and groin area (known as axillary or inguinal freckling), and skin-fold freckling are common skin manifestations.
- Neurological Symptoms: Neurofibromas, which are benign tumors that grow on or under the skin and along nerves, can cause pain, discomfort, and occasionally lead to nerve dysfunction. Plexiform neurofibromas are a type of tumor that can be larger and involve multiple nerves, potentially causing functional issues.
- Learning and Developmental Challenges: Some individuals with NF1 may experience learning disabilities or attention-related issues. However, these challenges can vary widely from person to person.
- Bone Abnormalities: Bone abnormalities like scoliosis (curvature of the spine), thinning of long bones, and other skeletal issues can occur.
- Eye Problems: NF1 can lead to vision problems, such as optic gliomas (tumors on the optic nerve) that may impact vision.
- Tumors in Other Organs: Some people with NF1 may develop tumors in other organs, like the brain, heart, or gastrointestinal tract, although these occurrences are relatively rare.
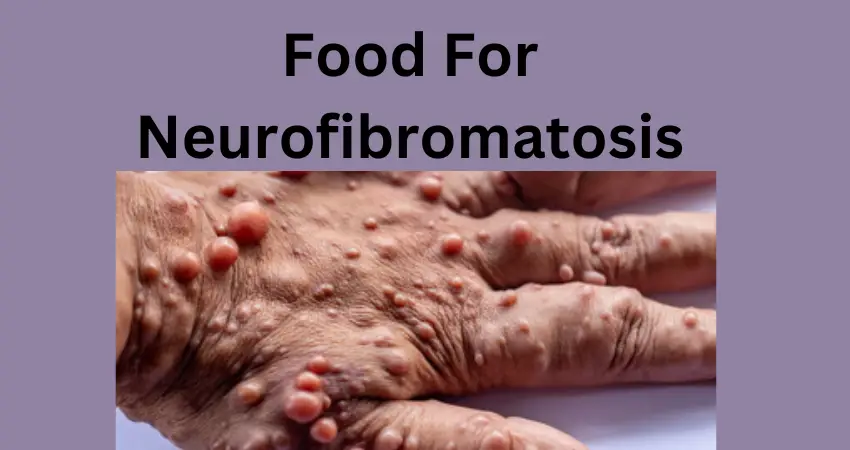
Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2):
NF2 is rarer than NF1 and is characterized by the development of tumors primarily on the auditory nerves (the nerves responsible for hearing and balance) and other nerves throughout the body. Key effects of NF2 include:
- Vestibular Schwannomas (Acoustic Neuromas): These tumors grow on the auditory nerves and can lead to hearing loss, balance problems, and tinnitus (ringing in the ears). As they grow, they may also compress nearby structures, leading to additional complications.
- Other Nervous System Tumors: Individuals with NF2 can develop tumors on other cranial and spinal nerves, potentially leading to a range of neurological symptoms depending on the location and size of the tumors.
- Vision Issues: NF2-related tumors can also impact the optic nerves, potentially leading to vision problems.
- Other Tumors: While NF2 primarily affects nerves, some individuals may develop non-nervous system tumors, although these occurrences are less common.
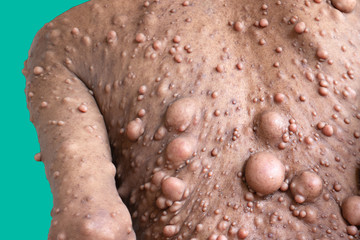
Neurofibromatosis is a genetic disorder that can cause the growth of tumors on nerve tissues.
While there’s no specific diet that can cure or treat neurofibromatosis, maintaining a healthy diet can support overall well-being. Here are some general guidelines on foods to consider:
Foods That Help With Neurofibromatosis
1. Nutrient-Rich Foods: A diet rich in nutrient-dense foods is crucial for overall well-being, especially for individuals with neurofibromatosis. Fruits and vegetables provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber that support various bodily functions. Whole grains offer sustained energy and promote digestive health, while lean proteins (such as poultry, fish, beans, and legumes) help with tissue repair and immune function. Healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil are beneficial for brain health and reducing inflammation.
2. Limit Processed Foods: Processed foods are often high in refined sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium. These additives can contribute to inflammation and increase the risk of obesity, which may exacerbate symptoms associated with neurofibromatosis. By reducing processed food intake, you’re giving your body a better chance to maintain balanced health and manage potential complications.
3. Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is essential for everyone, but it holds particular significance for those with neurofibromatosis. Proper hydration supports the nervous system’s functions and helps in the transmission of signals between nerve cells. Water also aids in flushing out toxins and waste products from the body, promoting overall detoxification.
4. Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Antioxidants play a vital role in combating oxidative stress, which can damage cells and contribute to various health issues. Including antioxidant-rich foods like berries, leafy greens, and vibrant vegetables in your diet provides your body with a defense against cellular damage and inflammation, which might indirectly benefit individuals with neurofibromatosis.
5. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Incorporating sources like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts into your diet can potentially help manage inflammation and improve overall health. These healthy fats also support brain health and might have a positive impact on nervous system function.

6. Calcium and Vitamin D: Maintaining strong bones is important for everyone, and individuals with neurofibromatosis may want to pay extra attention to bone health due to potential complications. Adequate calcium intake, along with sufficient vitamin D (which helps with calcium absorption), can help support bone density and minimize the risk of fractures.
7. Moderate Caffeine: Caffeine consumption should be moderate, as excessive caffeine intake might disrupt sleep patterns and increase nervousness. Good sleep is crucial for overall health, and proper rest can positively impact various bodily functions, including immune system support and tissue repair.
8. Limit Added Sugars: High levels of added sugars in the diet can lead to inflammation, weight gain, and potential metabolic issues. Minimizing the intake of sugary foods and beverages can help regulate blood sugar levels and support a balanced overall health status.
9. Balanced Portions: Eating in moderation and paying attention to portion sizes helps prevent overeating and maintain a healthy weight. This is particularly important for individuals with neurofibromatosis, as excess weight can put additional strain on the body and potentially worsen symptoms.
10. Consult a Professional: Individual nutritional needs vary based on genetics, health conditions, and other factors. Consulting a registered dietitian or healthcare provider can provide personalized guidance tailored to your specific situation. They can help you create a dietary plan that aligns with your health goals and works in harmony with your treatment plan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while there’s no specific diet to cure or treat neurofibromatosis, adopting a balanced and nutrient-rich eating pattern can contribute to your overall well-being.
Collaborating with healthcare professionals ensures that your dietary choices complement your medical care, enhancing your quality of life and supporting your journey with neurofibromatosis.
Always remember to communicate openly with your medical team about any dietary concerns or changes you’re considering.